[Java] DFS vs BFS
깊이 우선 검색(DFS)
- 연결된 항목으 끝까지 검색 후 상위 브랜치로 이동하여 검색을 진행
- 최대한 깊이 내려간뒤, 더이상 없을때 옆으로 이동하는 검색 형태
- Stack
넓이 우선 검색(BSF)
- 연결된 인접노드를 먼저 넓게 검색한 다음 더이상 없을때 하위로 내려감
- 최대한 넓게 이동 검색 후 하위로 이동.
- Queue
소스 코드
문제 그래프 연결 조건
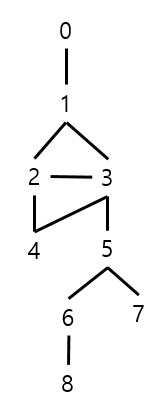
- DFS(0시작) 결과 : 0 1 2 4 3 5 6 8 7
- BFS(0시작) 결과 : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
DFS(Depth-First Search)
package dfsbfs;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Dfs { // Depth-First Search (inorder, preorder, postorder)
//Stack 사용
int cnt;
int[] ck; //방문 표시용
Queue<Integer>[] node; //node 관계 표시
Stack<Integer> st; // DFS용
public Dfs(int cnt) {
this.cnt = cnt;
this.ck = new int[cnt];
this.node = new LinkedList[cnt];
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
node[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
//DFS 용
st = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void addEdge(int a, int b) {
node[a].add(b);
node[b].add(a);
}
public void dfs() {
dfs(0);
}
public void dfs(int point) {
if(ck[point] == 1) return; //이미 방문
st.push(point);
ck[point] = 1;
int out_point = st.pop().intValue();
System.out.format("%d ", out_point);
//자식을 dfs에 재귀호출
while( ! node[out_point].isEmpty() ) {
int child = node[out_point].poll().intValue();
dfs(child);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dfs fs = new Dfs(9);//자료의 갯수
fs.addEdge(0,1);
fs.addEdge(1,2);
fs.addEdge(1,3);
fs.addEdge(2,4);
fs.addEdge(2,3);
fs.addEdge(3,4);
fs.addEdge(3,5);
fs.addEdge(5,6);
fs.addEdge(5,7);
fs.addEdge(6,8);
fs.dfs(0); //0 1 2 4 3 5 6 8 7
//fs.dfs(3); //3 1 0 2 4 5 6 8 7
}
}
// 출력
0 1 2 4 3 5 6 8 7
BFS(Breadth-First Search)
package dfsbfs;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Bfs { // Breadth-First Search
// Queue
int cnt;
int[] ck; //방문 표시용
Queue<Integer>[] node; //node 관계 표시
Queue<Integer> q;
public Bfs(int cnt) {
this.cnt = cnt;
this.ck = new int[cnt];
this.node = new LinkedList[cnt];
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
node[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
//BSF용
q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void bfs(){
bfs(0);
}
public void addEdge(int a, int b) {
//System.out.format("%d %d \n",a,b);
node[a].add(b);
node[b].add(a);
}
public void bfs(int point) {
if(ck[point] == 1 ) return;
q.add(point);
ck[point] = 1;
while( ! q.isEmpty() ) {
int out_piont = q.poll().intValue();
while( ! node[out_piont].isEmpty() ) {
int child = node[out_piont].poll().intValue();
//자식 노드들을 Q에 추가함
if( ck[child] == 0 ) {
ck[child] = 1;
q.add(child);
}
}//end whil
System.out.format("%d ", out_piont);
}//end while
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bfs fs = new Bfs(9);//자료의 갯수
fs.addEdge(0,1);
fs.addEdge(1,2);
fs.addEdge(1,3);
fs.addEdge(2,4);
fs.addEdge(2,3);
fs.addEdge(3,4);
fs.addEdge(3,5);
fs.addEdge(5,6);
fs.addEdge(5,7);
fs.addEdge(6,8);
fs.bfs(0); //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
//fs.bfs(3); //3 1 2 4 5 0 6 7 8
}
}
// 출력
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8